What is a laboratory sample pulverizer and how does it work?
In the world of material analysis, understanding a laboratory sample pulverizer is crucial. Dr. Emily Johnson, a leading expert in the field, once stated, "A laboratory sample pulverizer is essential for achieving accurate and reliable test results." This piece of equipment breaks down samples into fine powders, allowing for thorough testing.
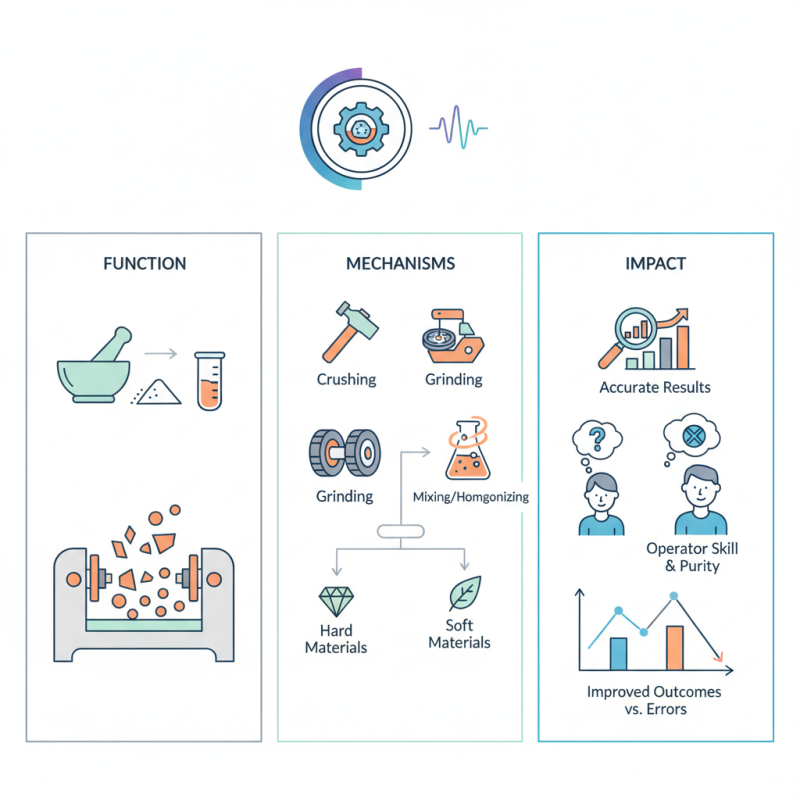
Typically, a laboratory sample pulverizer uses various mechanisms to crush and grind samples. Its design enables the processing of diverse materials, from minerals to soils. Precision is vital. However, the effectiveness often hinges on the operator's skill. Proper technique can yield better results, but mistakes can lead to contamination.
Laboratory sample pulverizers come in different types, each serving specific purposes. Some are more suited for hard materials, while others handle softer substances effectively. As important as these machines are, users must recognize their limitations. Understanding these nuances can improve analytical outcomes and avoid costly errors in research.
What is a Laboratory Sample Pulverizer?
A laboratory sample pulverizer is a vital tool in many scientific and industrial fields. It is used to grind, crush, or pulverize materials into fine particles. This device offers precise control over the particle size. Users can modify the settings to obtain desired results. The machine operates using mechanical force, often applying pressure or impact.
In practice, a pulverizer works by placing the sample within its chamber. Once activated, it utilizes moving parts to break down the material. The type of sample affects the process. For example, softer materials may pulverize quickly, while harder samples require more effort. The method of collection also matters. Some systems utilize bags or containers, while others may need manual collection.
Choosing the right pulverizer can be challenging. Different applications demand different specifications. What works well for one sample might not work for another. Users often encounter issues with uniformity. Particle size discrepancies can lead to inconsistent results. Over time, it becomes clear that adjustments are necessary to meet various requirements. Regular maintenance is essential to ensure optimal performance.
Key Components of a Laboratory Sample Pulverizer
A laboratory sample pulverizer is a vital tool in material analysis. Its primary function is to grind various samples into fine powders for testing. This process is crucial in labs that deal with geological, pharmaceutical, or chemical materials. The machine operates by using mechanical force to reduce the size of the samples.
Key components of a laboratory sample pulverizer include the grinding chamber, rotor, and power source. The grinding chamber is where the sample is placed. Its design often influences the efficiency of the pulverizing process. A well-constructed chamber can lead to more consistent results. The rotor spins at high speeds, generating enough force to break down the sample. Without a functional rotor, the whole system fails.
Despite its effectiveness, using a pulverizer is not always straightforward. Users may struggle to achieve the desired particle size. Sometimes, samples may not grind evenly, leading to variability in results. Regular maintenance is essential to avoid these issues. Ensuring the pulverizer is clean can prevent contamination. Proper adjustment of the settings is also key to obtaining accurate sample sizes.
Laboratory Sample Pulverizer Performance Comparison
Operating Principles of Laboratory Sample Pulverizers
Laboratory sample pulverizers are essential tools in various fields, including geology and material science. They serve to reduce the size of samples for further analysis. These pulverizers enable precise control over particle size. An industry report indicates that particle size distribution can significantly influence the results of chemical analyses. Fine particles ensure more accurate readings in tests involving assays.
Operating principles rely on mechanical force. The sample is placed in a chamber and subjected to grinding or crushing. Various mechanisms can be utilized, such as ball mills or disc mills. Each method offers unique benefits. For instance, ball mills are more suitable for hard materials, whereas disc mills perform well with softer samples. The speed and duration of grinding are crucial factors. Incorrect settings may lead to inconsistent particle sizes, affecting analysis quality.
Efficiency in sample preparation is paramount. According to research, inconsistent sample size can lead to a 20% variance in results. This uncertainty can affect critical decision-making in industries like mining. Thus, choosing the right pulverizer and understanding its operation are vital. Nonetheless, operators must regularly calibrate the devices. Neglecting maintenance could result in compounded errors over time, prompting a re-evaluation of methodologies used.
What is a laboratory sample pulverizer and how does it work? - Operating Principles of Laboratory Sample Pulverizers
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | Reducing materials to a fine powder |
| Types | Planetary, Jaw, Hammer |
| Applications | Mining, Environmental, Material Testing |
| Process | Sample feeds into the pulverizer, where it is crushed and ground by mechanical actions. |
| Advantages | High efficiency, consistent particle size, versatile |
| Maintenance | Regular cleaning, checking for wear on grinding components |
Applications in Material Science and Mining Industries
In material science and mining industries, the laboratory sample pulverizer plays a crucial role. This equipment is designed to grind samples into fine powders. Researchers and geologists rely on this machinery to prepare materials for testing. For instance, the Bureau of Mines reports indicate that precise sample preparation can improve the accuracy of analytical results by over 20%.
Applications in mining include analyzing ore samples and conducting mineral compositions. In laboratories, pulverizers help assess the properties of various materials. The granularity of the sample can directly impact test outcomes. Fine powders offer better reactivity in chemical processes. Operators must be mindful of this factor for reliable results.
Tip: Always calibrate your pulverizer before use. Regular maintenance ensures consistent performance. Also, be aware of sample contamination during grinding; it can skew your data. It's not merely about grinding but understanding the interactions between the material and the machinery.
Advantages and Limitations of Using Laboratory Pulverizers
Laboratory pulverizers are essential tools for sample preparation. They help achieve uniform particle sizes for analysis. However, like any equipment, they come with advantages and limitations.
On the positive side, pulverizers offer precision in grinding. This ensures that samples are ready for testing without contamination. They can handle various materials, including minerals and organic substances. However, the process can introduce heat. This heat may alter sensitive materials. Thus, temperature-sensitive samples require special attention.
Tips: Always monitor the pulverizer’s operation. Check for excessive heat to avoid damaging your sample. Also, make sure to clean the equipment thoroughly between uses. Contamination can skew results.
Despite their benefits, laboratory pulverizers have drawbacks. They may require frequent maintenance. The grinding elements can wear out, impacting performance. Additionally, the initial cost can be high. This might deter smaller labs from investing in them. Training staff to use the equipment properly is essential. Without proper training, mistakes can happen, leading to wasted samples and time.
